Training an Image Classification model - even with Deep Learning - is not an easy task. In order to get sufficient accuracy, without overfitting requires a lot of training data. If you try to train a deep learning model from scratch, and hope build a classification system with similar level of capability of an ImageNet-level model, then you'll need a dataset of about a million training examples (plus, validation examples also). Needless to say, it's not easy to acquire, or build such a dataset practically.
So, is there any hope for us to build a good image classification system ourselves?
Yes, there is!
Luckily, Deep Learning supports an immensely useful feature called 'Transfer Learning'. Basically, you are able to take a pre-trained deep learning model - which is trained on a large-scale dataset such as ImageNet - and re-purpose it to handle an entirely different problem. The idea is that since the model has already learned certain features from a large dataset, it may be able to use those features as a base to learn the particular classification problem we present it with.
This task is further simplified since popular deep learning models such as VGG16 and their pre-trained ImageNet weights are readily available. The Keras framework even has them built-in in the keras.applications package.
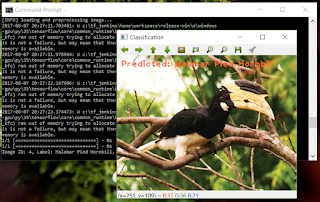 |
| An image classification system built with transfer learning |
The basic technique to get transfer learning working is to get a pre-trained model (with the weights loaded) and remove final fully-connected layers from that model. We then use the remaining portion of the model as a feature extractor for our smaller dataset. These extracted features are called "Bottleneck Features" (i.e. the last activation maps before the fully-connected layers in the original model). We then train a small fully-connected network on those extracted bottleneck features in order to get the classes we need as outputs for our problem.


